Climate changes in the high-resolution 20th century simulation
 Agulhas leakage is stronger in the present control simulations
Agulhas leakage is stronger in the present control simulationsMotivation
Previous studies suggest that leakage has increased since the late 1960s [Biastoch et al., 2009, Biastoch et al., 2015, Loveday et al., 2015], consistent with the observed changes in westerlies [Marshall 2003, Swart and Fyfe 2012]. We began to wonder if such changes exist in our climate change simulation HRC07. After all, none of the above-listed works were done with an ocean-eddy resolving coupled model like our in-house CCSM3.5.
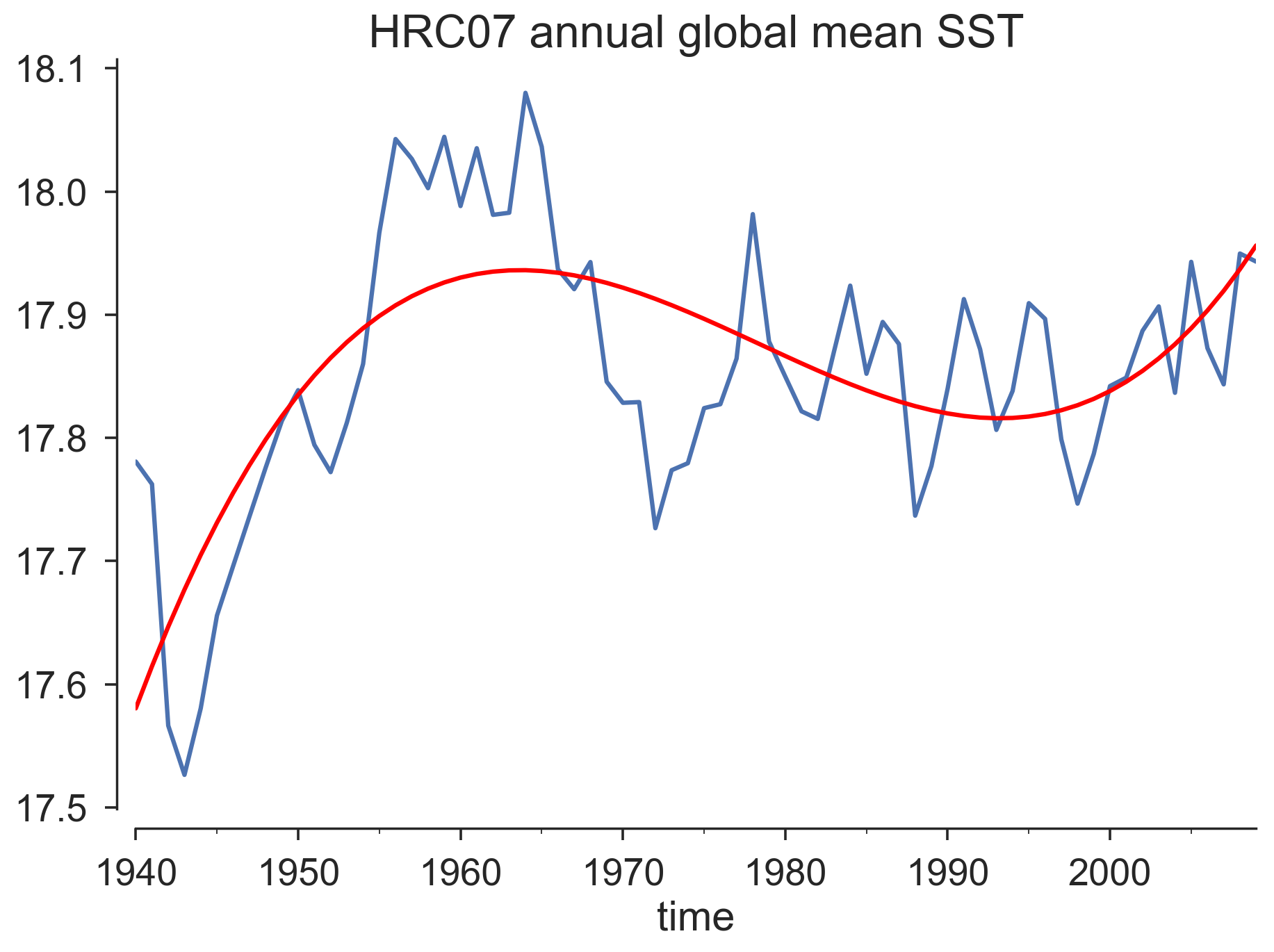
However, the early attempts revealed that the climate change simulation HRC07 suffered a lot from the spin-up process, specifically the global mean SST. The 10yr idle run before 1940 seems not enough. SST dives first before rising again and peaks around 1960. Therefore, instead of focusing on the linear trends of climate change run, we would like to use the two control runs to remove the common model drift between cases to isolate the real “warming signal” in the climate change simulation.
Method
Our work is based on a high-resolution configured Community Climate System Model (CCSM3.5) output. The spatial resolution of this simulation for the atmospheric and ocean component is 0.5 degree and 0.1 degree respectively. Three different runs are employed in this study: a 20th-century climate change simulation with observed CO2 forcing (HRC07), and two present-day control simulation with year-2000 CO2 forcing. All of them are initialized from the same spun-up year 2000 initial conditions, although at lower-resolution. Agulhas leakage is quantified using a Lagrangian particle tracking approach, more details can be found in Cheng et al. [2016].
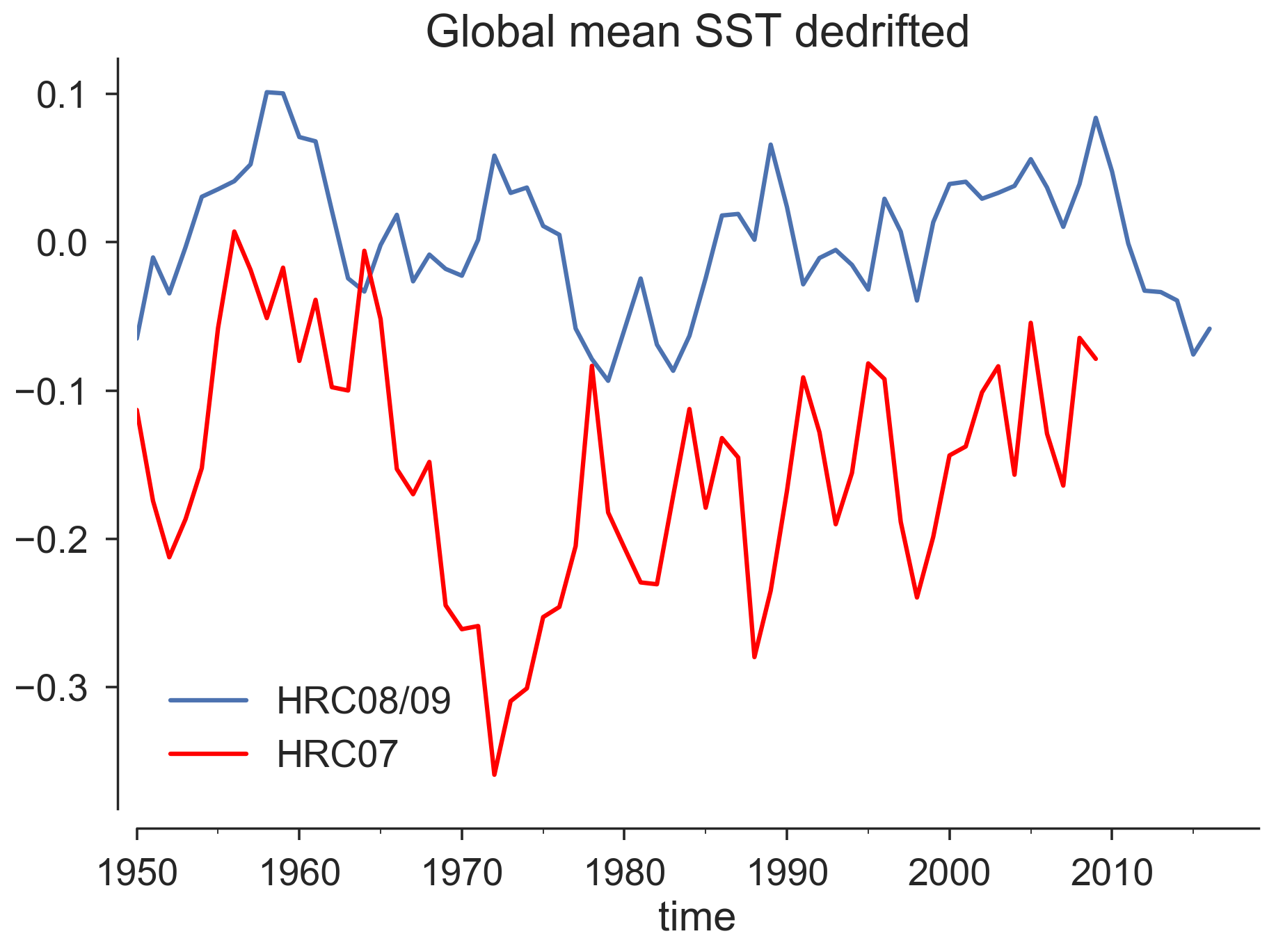
To remove the model drift in the HRC07, we take two approaches: (1) subtract HRC07 from the cubic spline fit of HRC08/09 and (2) takes the difference of (HRC08+HRC09)/2 -HRC07 at every timestep for many variables. It is expected that the difference might increase in first few years because the effect of high CO2 in the year 2000 is still lingering in HRC07. Global mean SST shown above is a good example. However, note that the equilibrium timescale differs from variable to variable. To rule out the initial-shock, we do not feel comfortable just rule out the first three decades.
So, instead of focusing on the linear trend based on regression of a prescribed period (which is usually very subjective), in this study, we will focus on the the changes between first 20 and last 20 years of the available record 1948-2007. First, we will focus on the differences in Agulhas leakage and westerlies, and try to compare such to the low-res CMIP5 historical CCSM run. Then we will progress to identify the changes in ocean circulation associated with the increasing AL in HRC07.
(developing)